Error mounting filesystem
After installing the ewf-tools the right way on a GNU/Linux Ubuntu machine, we executed the following command to create the ewf1 mounting point for our .E01 image:
mkdir /mnt/ewf;
ewfmount ./DISK.E01 /mnt/ewf/;
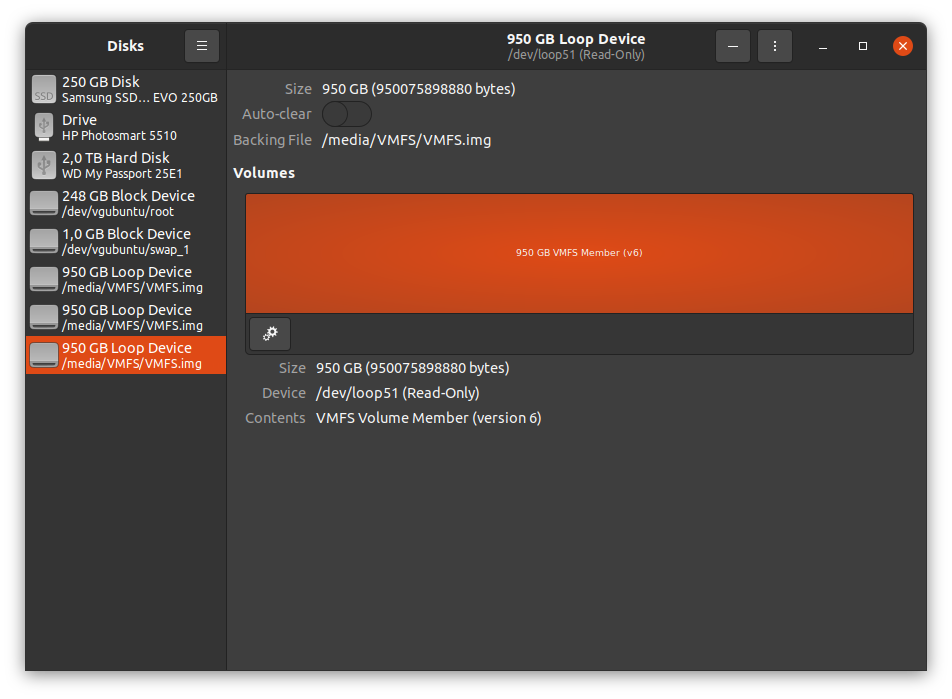
After the operating system created the mounting point, we opened the ewf1 file that appeared in /mnt/ewf/ using the Gnome Disk Image Mounter. This action made a new entry in the Gnome Disks Utility, showing our new disk.
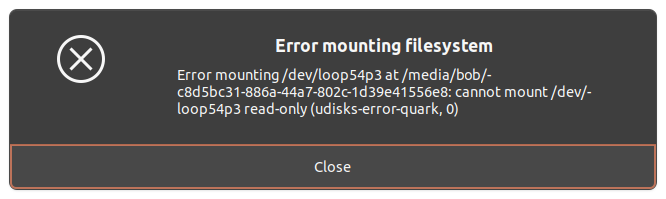
After clicking on the play button (labeled Mount selected partition) we got the following error:
We then tried to use the terminal to gain more control over the mounting parameters. To proceed with the following commands, we copied the Device value, which was /dev/loop54p3 in this case.
$ mkdir /mnt/loc;
$ sudo mount /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
mount: /mnt/loc: cannot mount /dev/loop54p3 read-only.
$ sudo mount -o ro /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
mount: /mnt/loc: cannot mount /dev/loop54p3 read-only.
$ sudo mount -o ro,loop /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
mount: /mnt/loc: cannot mount /dev/loop58 read-only.
$ sudo mount -o ro,loop -t ext4 /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
mount: /mnt/loc: cannot mount /dev/loop58 read-only.
$ sudo mount -o ro,norecovery,loop -t ext4 /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
The command that worked for us was the following:
sudo mount -o ro,norecovery,loop -t ext4 /dev/loop54p3 /mnt/loc;
The parameter that did the trick was norecovery. norecovery/noload instructs the system not to load the journal on mounting. Note that if the filesystem was not unmounted cleanly, skipping the journal replay will lead to the filesystem containing inconsistencies that can lead to any number of problems. This problem occurred because the machine did not shut down properly before it had its image cloned, so after we mount, we might not get the latest state of the disk.