ATEN – USB-to-Serial Converter (35cm) UC232A – Windows 10 (64bit) Drivers
Background
Recently we started using the UC232A USB-to-Serial Converter to connect to a board.
The software we used was TeraTerm on a 64bit Windows 10 without installing custom drivers.
Our serial port configuration was the following:
- Baud rate: 115200
- Data: 8 bit
- Parity: none
- Stop: 1 bit
- Flow control: none
- Transmit delay:
5 msec/char
5 msec/line
The problem
We noticed that something was wrong with the process as the terminal would not operate consistently.
Some times keystrokes did not appear on screen, in other times results would not appear correctly (they could be truncated or mixed with other data) and in general, the system acted like it was possessed by a ghost.
Troubleshooting
We played around with the configuration parameters, hoping that it was an issue like having the need to add large transmit delay but it did not change anything, the communication with the board was unstable.
Afterwards, we switched to another cable, of a different company, and everything worked as expected. The data on the screen was consistent and the ghost was banished. The UC232A was brand new so we tested that it works on a GNU/Linux machine, which turned out to be OK. Doing so, these two tests led us to the conclusion that since both the cable operates properly on GNU/Linux and the board operates properly using the other cable, that the issue we had was the automatically installed Windows 10 drivers.
Solution
While the cable was unplugged, we installed the official drivers we found here.
To find the drivers on that page, click on Support and Download tab at the bottom and then click on the Software & Drivers panel.
From the new table that will appear, under the category Windows Legacy Software & Driver we used the latest version that was available at the time that this post was written, which was v1.0.082 dated 2016-01-27 uc232a_windows_setup_v1.0.082.zip ([download id=”2357″] retrieved on the 23rd of November 2016).
After the download was finished, we restarted the machine, plugged in the cable and gave it another go.
The system was working as expected.
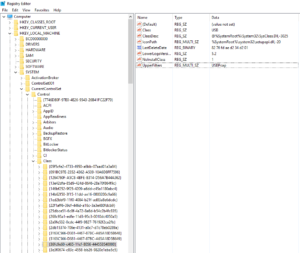
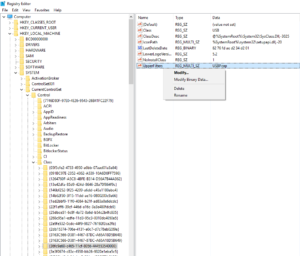
Following, you will find the screenshots from the device manager, after we got the cable working right.